8.3. 音标练习
这是一个 Jupyter Notebook,用来建立音标符号与声音之间的关联。
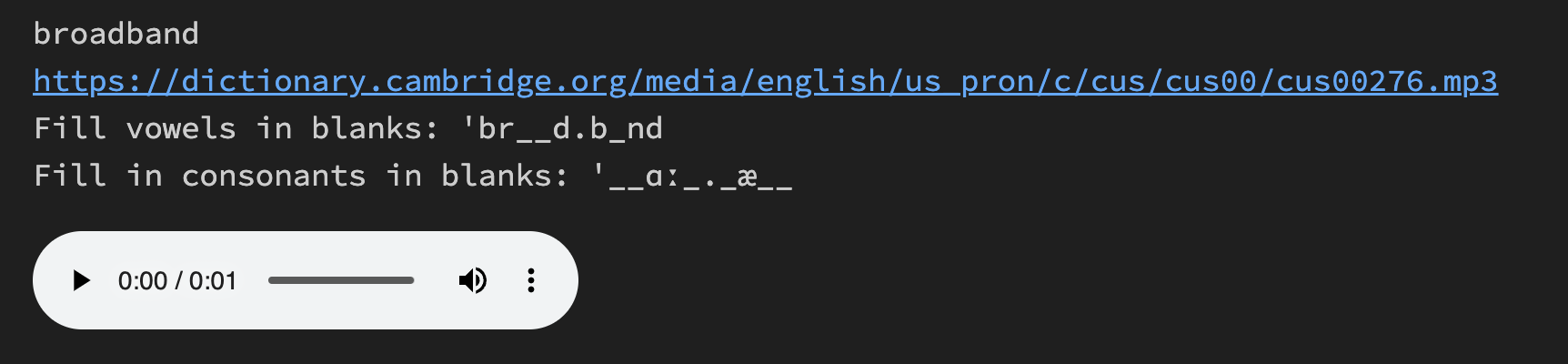
每次执行,随即从《剑桥英语发声词典》中选取一个词汇,播放真人朗读语音,而后要求对元音或者辅音填空……
执行结果如下:
Jupyter Notebook 代码如下:
Python
# %%
%pip install python-vlc
# %%
import requests
import json
import vlc
import re
import random
from IPython.display import Audio
import json
import requests
def load_json_database(source):
records = []
def parse_json_lines(lines):
for line in lines:
if line:
try:
record = json.loads(line)
records.append(record)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"Error parsing JSON: {e}")
try:
if source.startswith('http://') or source.startswith('https://'):
# Handle as URL
response = requests.get(source)
response.raise_for_status() # Raise an error for bad status codes
parse_json_lines(response.iter_lines(decode_unicode=True))
else:
# Handle as file
with open(source, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
parse_json_lines(file)
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"Error fetching data from URL: {e}")
except FileNotFoundError as e:
print(f"Error opening file: {e}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"An unexpected error occurred: {e}")
return records
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zelic91/camdict/main/cam_dict.refined.json"
json_database = load_json_database(url)
# %%
def search_in_json_database(database, search_word, region):
for record in database:
# 检查 word 字段是否匹配
if record.get('word') == search_word:
# 找到匹配项后,获取美式发音信息
pos_items = record.get('pos_items', [])
for pos_item in pos_items:
pronunciations = pos_item.get('pronunciations', [])
for pronunciation in pronunciations:
if pronunciation.get('region') == region:
# 找到美式发音,返回相关信息
return {
'pronunciation': pronunciation.get('pronunciation'),
'audio': pronunciation.get('audio')
}
# 如果没有找到匹配的 word 字段,返回 'not exist'
return 'not exist'
def replace_with_underscores(match):
return '_' * len(match.group(0))
# %%
# get a random word from the database
vowel_phonetics = re.compile(r'ɑː|ɑːr|ʌ||iː|ɪ|i|ɪr|ʊ|ʊr|uː|ʊr|e|er|æ|ə|ɚ|ɝː|ɒ|ɔː|ɔːr|ɔɪ|aɪ|aɪr|eɪ|aʊ|aʊr|oʊ|')
consonant_phonetics = re.compile(r'p|b|t|d|k|ɡ|f|v|θ|ð|s|z|ʃ|ʒ|tʃ|dʒ|r|h|l|t̬|j|w|ŋ|n|m|tr|dr|ts|dz|br|pr|fr|ɡr|θr|dr|ʃr|kr|bl|kl|ɡl|fl|pl|sl|sp|st|sk|sm|sn|sw|str|spr|skr|spl|sfr|skw|skr|skl|')
# if the word is with certain enddings such as 'es, ed, ing', get another word
random_word = random.choice(json_database)
while random_word['word'].endswith(('ed', 'ing', 'es', 'ts', 'ks', 'ds', 'ps', 'bs', 'gs', 'ls', 'rs', 'ms', 'ns', 'er', 'est')):
random_word = random.choice(json_database)
# get pronunciation of the random word with region 'us'
random_word_us = search_in_json_database(json_database, random_word['word'], 'us')
# get the word's phonetics
random_word_entry = random_word['word']
print(random_word_entry)
random_word_phonetics = random_word_us['pronunciation']
# get the audio url of the word
random_word_us_audio_url = random_word_us['audio']
print(random_word_us_audio_url)
blank_vowel_phonetics = re.sub(vowel_phonetics, replace_with_underscores, random_word_phonetics)
blank_consonant_phonetics = re.sub(consonant_phonetics, replace_with_underscores, random_word_phonetics)
# fill vowels in blanks
print(f'Fill vowels in blanks: {blank_vowel_phonetics}')
# fill consonants in blanks
print(f'Fill in consonants in blanks: {blank_consonant_phonetics}')
# play the audio
player = vlc.MediaPlayer(random_word_us['audio'])
player.play()
# display the audio
Audio(url=random_word_us_audio_url)